Why 8-Fiber MPO/MTP Solutions Are Your Path of Least Resistance
Filed under: Data Center
Comments: Comments Off on Why 8-Fiber MPO/MTP Solutions Are Your Path of Least Resistance
In looking at current and future applications – for both multimode and singlemode – it is easy to see that the foreseeable future will be dominated by 2- and 8-fiber solutions. Table 1 below clearly shows that the Ethernet Optical Transceiver Roadmap includes fiber applications that are always divisible by either 2 or 8 fibers. What does this mean for existing 12-fiber MPO/MTP connections?
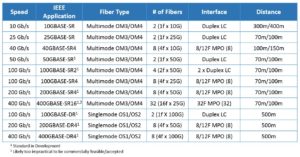
Table 1: Ethernet Optical Transceiver Roadmap includes multimode and singlemode fiber applications that are always divisible by either 2 or 8 fibers
For applications like 40 Gb/s (40GBASE-SR4) and 100 Gb/s (100GBASE-SR4) that are based on 8 multimode optical fibers, as well as future 400 Gb/s, the use of 12-fiber MPO/MTP solutions means that 33 percent of the optical fiber goes unused. One way that data center managers can ensure 100 percent utilization of optical fiber with 12-fiber MPO/MTP solutions is to use conversion cords or modules that transition two 12-fiber or one 24-fiber trunk from backbone cabling to three 8-fiber MPO/MTPs for connecting to 40 and 100 Gb/s equipment. This is ideal for those data centers that already deployed 12-fiber or 24-fiber backbone trunk cables. It should be noted however that conversion modules introduce additional insertion loss into the channel and conversion cords mean that three ports need to be taken off line in the event that the cord needs to be replaced.
On the other hand, 8-fiber MPO/MTP solutions that are starting to hit the market are considered the most efficient option since they support current and future duplex fiber applications using modules that break out 8-fiber MPO/MTPs to duplex LCs, as well as current and future 8-fiber applications without the need for conversion cords or modules.
